These answer explanations are and always will be free. However, given multiple email requests, I will post my Venmo (@Adam-Zakaria-SLO) if you want to send a few dollars to show your support for the website.
I also offer reasonably priced Study Guides and Personalized Study schedules, so please reach out using the Tutoring menu option or Study Guides and Personalized Study schedules menu option listed above if you would like personalized support.
Furthermore, I offer personal statement and application review services for residency applicants, so please reach out using the “Residency Advising and Application Preparation” menu option above if interested.
Lastly, please check out my Youtube channel (https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCT1Ukl4pm5QK9iw6h4MB_Hw/playlists) and the “Biostatistics Curriculum” option above for free videos and practice questions reviewing all the essential biostatistics topics covered on NBME exams. Good luck with your exams!
1) An otherwise healthy 52-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department 3 hours after the sudden onset of severe…
Lumbar laminectomy
- Young woman presents with sudden onset of lower back pain and is found to have shooting pain down one leg, saddle anesthesia (numbness over perineum), and loss of Achilles reflex on the left with imaging concerning for spinal compression, which represents cauda equina syndrome –> Manage with glucocorticoids + surgical correction
- Key idea: Cauda equina syndrome is due to compression of spinal roots L2 and below and classically presents with back pain + saddle anesthesia + reduced reflexes + bowel/bladder dysfunction
- Key idea: Any time you are concerned about spinal cord compression in the setting of trauma/inflammation, you should start IV glucocorticoids because it helps to limit compression of the spinal cord
- Red flag symptoms for back pain –> TUNA FISH
- Trauma
- Unexplained weight loss
- Neurologic findings
- Age > 50
- Fever
- IVDU
- Steroid usage
- History of cancer
2) A 72-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department 6 hours after the onset of double vision, loss of balance…
Vertebral
- Elderly woman with atherosclerotic risk factors presents with acute onset of diplopia, loss of balance and dizziness concerning for vertebrobasilar insufficiency
- Key idea: Posterior circulation supplies blood to the cerebellum, brain stem and visual cortex, which is why it can lead to cerebellar signs, visual symptoms and possible brain stem stroke syndromes
- Subclavian atherosclerosis –> Subclavian steal syndrome –> Syncope and arm pain when using the ipsilateral arm due to retrograde blood flow
- Middle cerebral artery occlusion –> Upper extremity and face weakness + sensory changes with aphasia (if left-sided) or left hemi-neglect (if right-sided)
3) A 57-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department 20 minutes after a simple partial seizure…
Meningioma
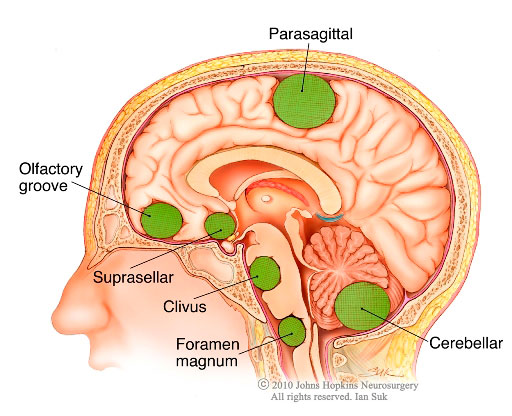
- Middle-aged woman brought in following a seizure found to have a uniform, enhancing parasagittal mass most concerning for a meningioma
- Key idea: Meningiomas (as the name implies) tends to occur on the outer surface of the brain (rather than within the parenchyma) given they are derived from the meninges
- Schwannoma –> Classically present in brainstem and pontomedullary junction (thereby compressing CN 5, 7 and/or 8)
4) Over the past 3 months, a 40-year-old woman has had multiple 1- to 2-minute episodes of numbness and tingling…
Parietal lobe
- Young woman presents with a partial seizure with sensory symptoms without loss of consciousness, which most likely originates from the somatosensory cortex located in the anterior portion of the parietal lobe
- Partial motor seizures originate from the primary motor cortex in the posterior frontal lobe
- Temporal lobe seizures –> Olfactory and/or auditory aura preceding seizure-like activity (classically smelling burnt rubber or hearing hissing noises)
5) A 27-year-old nulligravid woman has had café au lait spots and multiple neurofibromas since birth. A diagnosis of…
50% for each child, since neurofibromatosis is autosomal dominant
- Key idea: Both neurofibromatosis Type 1 and Type 2 are autosomal dominant disorders
- Neurofibromatosis Type 1 –> Neurofibromas, Cafe-au-lait spots, Optic gliomas, Lisch nodules, pheochromocytomas
- Neurofibromatosis Type 2 –> Bilateral schwannomas
6) A 37-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 1-week history of moderate low back pain. He thinks he may have hurt…
Continuation of ibuprofen therapy
- Young man presents with 1-week of back pain following yard work with exam demonstrating paraspinal muscle tenderness, most consistent with MSK-related lower back pain –> Manage with 4-6 week trial of NSAIDs and remaining active (prolonged bed rest should be avoided)
- Key idea: Vertebral point tenderness consistent with fracture, malignancy and osteomyelitis/epidural abscess, but paraspinal muscle tenderness most consistent with MSK-related back pain
- Key idea: Opiates should generally be avoided for acute low back pain
7) A 77-year-old man comes to the physician because of increasingly severe low back pain for 3 months…
Epidural metastatic carcinoma
- Elderly man with 120 pack-year smoking history presents with severe back pain with signs consistent with spinal cord compression at the T9 level (sensory loss below that level, UMN signs in lower extremities, bladder/bowel dysfunction) with vertebral tenderness concerning for metastatic cancer to the spine complicated by spinal cord compression
- Key idea: Back pain with vertebral tenderness can be due to fracture, metastatic malignancy or osteomyelitis/epidural abscess
- Key idea: Next best step in management would typically be IV glucocorticoids to try to minimize degree of spinal cord compression
- Red flag symptoms for back pain –> TUNA FISH
- Trauma
- Unexplained weight loss
- Neurologic findings
- Age > 50
- Fever
- IVDU
- Steroid usage
- History of cancer
8) A 17-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department by ambulance 2 hours after he dove into a shallow lake and struck the back…
Bilateral dislocation of facets with impingement of the left C6 nerve root
- Adolescent who struck head and presents with wrist extension weakness and sensory loss to the radial aspect of the forearm and thumb with imaging showing obvious step-off between 5th and 6th vertebrae, concerning for C6 nerve root injury
- Key idea: In the cervical spine the nerve root comes out above the associated vertebrae (AKA C6 nerve root comes out above the C6 vertebral body), whereas in the thoracic/lumbar/sacral spine the nerve root comes out below the associated vertebrae
- Key idea: C6 nerve root provides sensation to the thumb( you hold your thumb up, your hand looks like a 6!)
9) A 32-year-old man comes to the physician 2 hours after the onset of dizziness, nausea, and unsteadiness. He had a whiplash neck…
Left vertebral
- Young man receiving chiropractic manipulations of the neck presents with acute dizziness, unsteadiness, voice hoarseness, miosis of the left pupil and decreased sensation over the left face and right extremities, concerning for left lateral medullary syndrome due to left vertebral artery dissection
- Key idea: Chiropractic manipulation can lead to dissection of cerebral/vertebral arteries
- Key idea: “Crossed signs” of loss of pain/temp sensation on one side of face and opposite side of body concerning for brainstem lesion
- Key idea: CN 9/10 deficit specific for lateral medullary syndrome, whereas CN 7 deficit more specific for lateral pontine syndrome
- Key idea: Lateral brainstem lesions can lead to damage to sympathetic tracts, leading to ipsilateral Horner’s syndrome (miosis, ptosis, anhidrosis)
10) One month after starting isoniazid and rifampin therapy for pulmonary tuberculosis, a 62-year-old woman develops…
Vitamin B6
- Middle-aged man on TB therapy presents with paresthesias and microcytic anemia, concerning for Vitamin B6 deficiency due to isoniazid treatment
- Key idea: Vitamin B6 deficiency –> Sideroblastic anemia (microcytic anemia) and paresthesias
- Key idea: Patients receiving RIPE therapy should also receive pyridoxine (vitamin B6)
11) An 82-year-old man is brought to the emergency department 1 hour after he collapsed while walking in his garden…
The patient should be made DNR and extubated, and fluids should be withdrawn as he wishes
- Key idea: Patient autonomy is almost always prioritized, so if a patient has decision-making capacity then we should respect their wishes
- Note: One specific example where autonomy is not prioritized includes when patients are a risk to themselves or others, including from a public health standpoint (e.g., patients with meningococcemia or tuberculosis not being allowed to leave hospital)
12) A 22-year-old man who is a collegiate volleyball player comes to the physician because of a 2-month history of…
Irritation of the suprascapular nerve
- A young man with significant amounts of overhead exercises/movements presents with chronic progressive shoulder pain with weakness in external rotation and initiation of abduction of the shoulder, most consistent with suprascapular nerve irritation
- Key idea: Suprascapular nerve supplies 2 of the rotator cuff muscles, specifically the supraspinatus (mediates initial shoulder abduction) and infraspinatus (mediates external shoulder rotation)
- Rotator cuff tendinitis –> Full active and passive range of motion, but pain with movement
- Rotator cuff tear –> Incomplete active ROM with complete passive ROM
- Adhesive capsulitis (“Frozen shoulder”) –> Elderly patient with reduced active AND passive range of motion
13) A 37-year-old woman has had throbbing right-sided headaches that began gradually 6 weeks ago and have increased…
Brain tumor
- Young woman with chronic progressive headaches that are worse in the morning with left arm pronator drift, which is concerning for a brain tumor (likely near the right temporal lobe)
- Key idea: Headache that is worse in the morning and associated with nausea is concerning for elevated intracranial pressure given that ICPs are highest after laying flat overnight without gravity promoting drainage of CSF and blood from the brain
- Key idea: Pronator drift assesses for an upper motor neuron lesion, and if positive indicates a problem in the spinal cord, brainstem or brain
- Idiopathic intracranial hypertension –> Overweight middle-aged woman with headache and nausea in the morning + papilledema
14) A previously healthy 45-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department 1 hour after she lost consciousness while…
Lumbar puncture
- Young woman presents with acute loss of consciousness associated with a severe headache, photophobia and meningismus with a normal CT scan who should be further worked up with a lumbar puncture to differentiate between subarachnoid hemorrhage and meningitis
- Key idea: Both subarachnoid hemorrhage and meningitis can present with headache, meningismus (painful neck movements) and fever –> In this case given the lack of fever or obvious exposures (college dormitory, summer camp, etc.) I would lean towards non-traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage due to an aneurysmal rupture
- Key idea: If patient presents with worst headache of their life, always consider subarachnoid hemorrhage!
15) A 77-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 3-year history of increasingly severe pain, swelling…
Radiation-induced brachial plexopathy
- Elderly woman with history of radiation to the chest wall who presents with swelling of the left upper extremity which is adducted, extended and internally rotated, consistent with radiation-induced Bell’s palsy (C5-C6 nerve root damage)
- Key idea: Swelling in the upper extremity due to lymphedema in the setting of mastectomy (given axillary lymph nodes are often removed)
- Spinal stenosis –> Back pain that is improved with back flexion, often seen in elderly patients
- Syringomyelia –> Cyst-like space in the cervical spine leading to hand weakness and loss of pain/temperature in a “cape-like distribution” of the back and upper extremities
16) A 67-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by his wife 30 minutes after a 15-minute episode of inability…
Embolus from a ventricular aneurysm
- Elderly man with recent left ventricular MI presents following an episode of aphasia and is found to have no significant heart murmurs and mild stenosis of the left carotid artery, suggesting that embolic source may be from left ventricular aneurysm
- Key idea: Left anterior descending occlusion –> Left ventricular muscle death –> Increased stasis of blood near anterior left ventricular wall –> Increased propensity for clot formation
- Key idea: Common sources of emboli to the brain include:
- Atrial fibrillation (leads to clot in left atrial appendage)
- Carotid atherosclerosis (often leads to recurrent episodes of ipsilateral monocular blindness [amaurosis fugax])
- Endocarditis
- LV aneurysm
- Key idea: First step in setting of stroke is whether it is embolic versus hemorrhagic, which can be distinguished by performing a non-contrast head CT (which should detect bleeding) and paying attention to timing (embolic will be maximal intensity from the beginning whereas hemorrhagic worsens over hours)
- Lacunar infarct –> Pure motor stroke or pure sensory stroke
17) A 10-day-old newborn is brought to the emergency department 1 hour after a seizure that involved clonic jerking…
Neonatal herpes simplex encephalitis
- Newborn baby presents with multiple seizures and altered mental status with CSF demonstrating normal CSF glucose level, mildly increased leukocyte count and elevated RBC count, consistent with possible HSV encephalitis
- Key idea: Normal CSF glucose should be ~2/3 of blood glucose, so given a normal blood glucose is around 100 a normal CSF glucose is around 60-70
- CSF findings of infectious pathogens:
- Bacterial: Neutrophilic predominance, really high WBCs, low glucose
- Fungal/Mycobacterial: Lymphocytic predominance, low glucose
- Viral: Lymphocytic predominance, normal glucose
- Key idea: HSV encephalitis often leads to hemorrhage of the temporal lobes, and therefore leads to increased CSF RBC count
18) A 72-year-old man with a 10-day history of fever, nausea and vomiting, and progressive confusion remains hospitalized…
Tuberculous meningitis
- Elderly man who is immunosuppressed in setting of steroid usage presents with subacute fever and confusion refractory to broad-spectrum antibiotics with CSF findings of lymphocytic predominance with extremely low glucose level most consistent with fungal or mycobacterial meningitis
- CSF findings of infectious pathogens:
- Bacterial: Neutrophilic predominance, really high WBCs, low glucose
- Fungal/Mycobacterial: Lymphocytic predominance, low glucose (Tb leads to particularly low CSF glucose)
- Viral: Lymphocytic predominance, normal glucose
- Neurosyphilis –> Should be responsive to steroids
- Lyme disease –> Bilateral bell’s palsy
19) A 52-year-old man is brought to the emergency department because of a 4-day history of progressive numbness and…
Metastatic spinal cord compression
- Middle-aged man with history of cancer presents with bilateral lower extremity weakness with lower extremity UMN signs (Babinski, hyperreflexia) and decreased sensation below the nipple line, most concerning for spinal cord injury at around the T10 level with metastatic disease to the vertebral spine being the most likely etiology
- Key idea: UMN signs indicative of disease at level of spine, brainstem or brain
- Key idea: Back pain with point tenderness to the vertebral spine can be caused by:
- Fracture
- Osteomyelitis
- Metastatic disease to bone
- Guillain-Barre syndrome –> Ascending weakness and sensory changes with loss of reflexes
- Myopathy –> Proximal muscle weakness without sensory changes
20) A 57-year-old man comes to the physician 2 hours after the sudden onset of visual loss in the right eye. He has no history of similar…
Central retinal artery occlusion
- Middle-aged man with atherosclerotic risk factors presents with sudden onset visual loss with a cherry-red spot on the macula most concerning for central retinal artery occlusion
- Key idea: Cherry-red spot occurs because the retina is relatively hypoperfused except at the macula given it has its own blood supply, with the 3 main causes being:
- Central retinal artery occlusion
- Tay-Sachs disease
- Niemann-Pick disease
21) A 67-year-old woman comes to the physician because of excessive sleepiness and fatigue. She has required more sleep for several…
Methylphenidate
- Elderly woman with chronic history of falling asleep unexpectedly and cataplexy (muscle paralysis with preserved consciousness often in setting of laughing/coughing) most concerning for narcolepsy –> Treat with stimulant such as methylphenidate or modafinil
- Key idea: Narcolepsy defined by recurrent lapses into sleep/naps along with:
- Cataplexy
- Low CSF levels of hypocretin-1
- Shortened REM sleep latency on polysomnography
22) A 6-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department 20 minutes after a motor vehicle collision in which he was the unrestrained front…
Cerebral concussion
- Young boy who had a traumatic head strike with immediate loss of consciousness but who has a normal neurologic exam, most consistent with a concussion
- Key idea: Concussions represent a mild form of traumatic brain injury and should NOT lead to focal neurologic findings –> Presence of focal neurologic findings or deterioration in mental status should prompt concern for potential bleeds (including epidural hematomas)
- Key idea: Patients with concussions can have non-specific symptoms (fatigue, poor sleep, trouble concentrating) that persists for months after the incident
- Epidural hematoma –> Strike to the side of the head leading to immediate loss of consciousness with “lucent period” lasting minutes-hours followed by rapid deterioration in mental status as blood accumulates in the epidural space
23) A 37-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 4-month history of headaches and blurred vision. She has…
Impaired resorption of CSF
- Young overweight woman with oligomenorrhea (irregular menstrual periods) presents with headaches and blurred vision with work-up notable for papilledema and elevated CSF opening pressure with normal ventricular size on CT, consistent with idiopathic intracranial hypertension –> Due to impaired resorption of CSF
- Key idea: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (AKA pseudotumor cerebri) almost always occurs in overweight young women, with risk factors being remembered with the mnemonic TOAD (Tetracycline antibiotics, Obesity, vitamin A analogs (e.g., isotretinoin), Danazol)
- Signs/symptoms concerning for elevated intracranial pressure:
- Papilledema (blurred optic disc)
- Headache and nausea worse in the morning (given accumulation of CSF and blood in brain caused by laying flat overnight)
24) A 62-year-old man is brought to the emergency department because of progressive weakness of his legs during the past…
Removal of the catheter
- Middle aged man with percutaneous tunneled dialysis catheter presents with fevers, leg weakness, UMN signs in the lower extremities and tenderness to percussion over the lumbar spine, with imaging demonstrating a lumbar epidural abscess –> Given most common pathogen in setting of epidural abscess is Staph aureus, most likely source of sepsis is due to a line infection so the dialysis catheter should be removed to achieve source control
- Point tenderness over the spine can be due to:
- Osteomyelitis/Epidural abscess
- Fracture
- Metastatic disease to bone
25) A 72-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 2-day history of pain in the left thigh and flank and weakness…
Femoral nerve
- Elderly woman with type 2 diabetes presents with weakness of the iliopsoas and quadriceps muscles, decreased quadriceps reflex and decreased sensation over the lateral thigh and medial calf, most consistent with femoral neuropathy
- Mnemonic to remember nerve roots responsible for common reflexes:
- C5-C6, pick up sticks (biceps reflex)
- C7-C8, lay them straight (triceps reflex)
- L3-L4, kick the door (quadriceps)
- L5-S1, jump for fun (Achilles)

26) A 27-year-old man is admitted to the hospital because of a 4-week history of difficulty with speech and weakness of his…
Central nervous system lymphoma
- Young man with history of HIV presents with unilateral neurologic symptoms (aphasia, UMN weakness of right leg) and is found to have multiple ring-enhancing lesions refractory to treatment with pyrimethamine-sulfadiazine, most consistent with CNS lymphoma
- Key idea: If a patient with HIV presents with ring-enhancing lesions in the brain, the two diagnostic considerations are toxoplasmosis versus CNS lymphoma:
- Toxoplasmosis: Multiple lesions responsive to pyrimethamine-sulfadiazine, patients with poorly controlled HIV
- CNS lymphoma: Single-multiple lesions unresponsive to pyrimethamine-sulfadiazine
27) A 67-year-old semiretired corporate executive comes to the physician with his wife because she is concerned about his…
Dementia, Alzheimer type
- Elderly man presents with chronic history of memory problems with exam consistent with word-finding difficulty and short-term memory deficits, most consistent with Alzheimer dementia
- Key idea: Two most common causes of dementia are Alzheimer disease (chronic, gradual worsening of memory without neurologic findings) and Vascular dementia (stepwise worsening with associated neurologic findings)
- Key idea: If memory changes begin to cause distress or disrupt normal functioning, then it is no longer normal aging
28) A 67-year-old man is brought to the physician by his wife because of a 1-month history of deafness, ringing in both ears…
Aminoglycoside-induced ototoxicity
- Elderly man with recent treatment with gentamicin (aminoglycoside) presents with nystagmus, ataxia and bilateral sensorineural hearing loss (air conduction > bone conduction), most consistent with aminoglycoside-induced ototoxicity with an associated vestibulotoxicity
- Two types of hearing loss:
- Sensorineural: Disease affecting the inner ear, CN8, brainstem or brain (e.g., age-related hearing loss, drug-related ototoxicity, schwannoma)
- Air conduction > Bone conduction on Rinne testing
- Conductive: Disease affecting the external or middle ear (e.g., cerumen impaction, serous otitis media, cholesteatoma)
- Bone conduction > Air conduction on Rinne testing (given noise would have trouble traveling from external ear –> middle ear –> inner ear)
- Sensorineural: Disease affecting the inner ear, CN8, brainstem or brain (e.g., age-related hearing loss, drug-related ototoxicity, schwannoma)
- Meniere’s disease –> Intermittent minutes-hours long episodes of vertigo associated with tinnitus and hearing loss
29) A 42-year-old woman with AIDS comes to the physician because of a 2-week history of progressive right-sided weakness…
Toxoplasmosis
- Young woman with AIDS presents with unilateral neurologic symptoms and increased intracranial pressure with CT exam showing multiple ring-enhancing lesions, most consistent with toxoplasmosis
- Key idea: If a patient with HIV presents with ring-enhancing lesions in the brain, the two diagnostic considerations are toxoplasmosis versus CNS lymphoma:
- Toxoplasmosis: Multiple lesions responsive to pyrimethamine-sulfadiazine, patients with poorly controlled HIV
- CNS lymphoma: Single-multiple lesions unresponsive to pyrimethamine-sulfadiazine
30) A 47-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by his friend 30 minutes after being found unconscious in his bed…
Hyperbaric oxygen
- Middle-aged man living in a trailer park presents after being found unconscious without any localizing neurologic symptoms concerning for carbon monoxide –> Treat with hyperbaric oxygen to displace carbon monoxide
- Key idea: Carbon monoxide classically leads to altered mental status + headache + red skin with SpO2-PaO2 dissociation (given SpO2 cannot differentiate between oxyhemoglobin and carboxyhemoglobin, so will overestimate oxygen saturation)
- Methylene blue –> Methemoglobinemia (patient who takes new drug (sulfa, benzocaine, etc.) and presents with central cyanosis unresponsive to oxygen)
- Naloxone –> Opioid intoxication (respiratory depression, pinpoint pupils)
- Physostigmine –> Anticholinergic toxicity (tachycardia, dry skin, mydriasis, etc.)
- Vitamin B1 (thiamine) –> Wernicke encephalopathy (confusion, ataxia, ophthalmoplegia)
31) A 52-year-old woman comes to the physician because of facial numbness for 2 weeks. Her symptoms began as a “funny feeling”…
Mandible
- Middle-aged woman with history of metastatic breast cancer with supraclavicular adenopathy (concerning for metastatic caner) presents with decreased sensation over the left chin, concerning for compression/dysfunction of cranial nerve V3 due to metastatic spread to the mandible leading to compression
- Brachial plexus –> Upper extremity symptoms
- Cerebellopontine angle (e.g., Schwannoma) –> Defects with CN5, CN7 and/or CN8

32) A 72-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 3-month history of increasingly depressed mood, fatigue…
Bupropion
- Elderly man with Parkinson disease who would like to quit smoking presents with signs/symptoms of major depression, and therefore would best be treated with bupropion
- Key idea: SSRIs, SNRIs, Bupropion, and Mirtazapine are all first-line antidepressants, so selection should be based on the side effect profile
- SSRIs –> Generally well-tolerated and often first-line if patient doesn’t have compelling indication for other first-line antidepressant
- SNRIs –> Duloxetine useful in patients with neuropathic pain (e.g., diabetes)
- Bupropion –> Leads to less weight gain, less sexual side effects and helps patients quit smoking
- Mirtazapine –> Promotes increased sleep and appetite, often useful in elderly patients
33) A previously healthy 6-month-old girl is brought to the emergency department by ambulance because of difficulty breathing…
Shaken baby syndrome
- Young baby brought to the emergency department after a short fall is found to have bilateral retinal hemorrhages and a bulging anterior fontanelle with imaging concerning for a subdural hemorrhage, most concerning for shaken baby syndrome
- Key idea: Bilateral retinal hemorrhages is basically pathognomonic for shaken baby syndrome
- Key idea: Subdural hematomas occur in the setting of tears to the bridging veins, and are often seen among shaken baby syndrome patients (given rapid acceleration-deceleration injury to the brain) and elderly patients with falls (given elderly patients have cerebral atrophy –> Decreased protection of bridging veins –> Increased risk for rupture)
- Key idea: Child abuse should be considered when the mechanism of injury described by the caregiver cannot explain the degree of injury or are not compatible with a child’s milestones (e.g., parents saying a 9 month old ran into a wall)
34) An 8-month-old girl is brought to the physician by her parents because of increased irritability over the past month…
Degeneration of the white matter
- Infant with parents who are related presents with progressive irritability and is found to have pale optic nerves, increased spasticity and UMN signs concerning for Krabbe disease (lysosomal storage disease associated with white matter degeneration due to demyelination)
- Periventricular calcifications –> Congenital CMV (microcephaly, seizures, etc.)
- Hydrocephalus –> Altered mental status + Increased head size
- Holoprosencephaly –> Present at birth, patient has CNS that is not divided into two and therefore should have single eye
- Cerebellar hypoplasia –> Ataxia
35) A 72-year-old right-handed woman is brought to the emergency department 30 minutes after the onset of double vision…
Left midbrain
- Elderly woman presents with sudden onset visual changes and right-sided weakness and is found to have left ptosis, impaired left eye movements, dilated left pupil and UMN symptoms on the right upper and lower extremities, most consistent with a left medial midbrain injury
- Key idea: When patients have “crossed signs” (neurologic deficits affecting opposite sides of the body above and below the neck) often concerning for a brainstem injury (given many of the tracts cross in the brainstem/medulla)
- Key idea: Left ptosis with “down and out” pupil and left eye dilation consistent with CN3 injury given it provides motor component to eye movements, eyelid elevation and parasympathetic tone
- HIGH-YIELD: Rule of 4’s below can help you develop system for localizing brainstem lesions (recommend Boards & Beyond video)
- Key idea:
- Medial midbrain –> CN3 and CN4 defects
- Medial pons –> Locked-in syndrome
- Lateral pons –> CN7 defect is specific finding
- Medial medulla –> CN12 defect is specific finding
- Lateral medulla –> CN 10/11 defect is specific finding

36) A 67-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 7-month history of progressive bilateral leg pain. She describes…
MRI of the lumbar spine
- Elderly woman with cardiac risk factors presents with chronic history of bilateral buttock, thigh and calf pain that worsens with activity and is relieved by leaning forward, most consistent with pseudoclaudication in the setting of spinal stenosis –> Diagnosed via lumbar MRI
- Key idea: Both claudication due to peripheral artery disease and pseudoclaudication due to spinal stenosis will present with exertional leg pain, with differentiating factors including:
- Claudication (PAD)
- Cardiac risk factors (diabetes, HTN, smoking, etc.)
- Reduced lower extremity pulses and temperature
- Reduced hair on legs (indicative of decreased perfusion)
- Pain worse in the calves (distal blood supply affected most strongly)
- Pseudoclaudication (spinal stenosis)
- Positional pain (worse with extension, better with flexion)
- Pain affecting the buttocks/thighs
- Claudication (PAD)
37) Over the past 6 months, an otherwise healthy, 19-year-old cheerleader has had increasingly severe neurologic symptoms…
Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculopathy
- Young woman presents with chronic progressive lower extremity weakness and sensory changes with decreased lower extremity reflexes with slowed peroneal motor conduction most concerning for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy
- Key idea: Guillain-Barre is also called acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy, so chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculopathy has basically the same presentation (lower extremity weakness, sensory changes and loss of reflexes, increased CSF protein with normal WBC count [albuminocytologic dissociation]) but extended over a longer time period
- While Guillain-Barre often has an obvious trigger (GI infection, vaccination, etc.), CIDP is often idiopathic
38) A 67-year-old woman comes for a routine health maintenance examination. She is concerned about developing dementia because…
Continued control of blood pressure
- Key idea: #1 risk factor for stroke/TIA is hypertension
- Key idea: #1 risk factor for atherosclerotic disease (MI, PAD, etc.) is smoking > diabetes
39) A 32-year-old woman comes to the physician with her husband because of a 6-month history of fluctuating symptoms including…
MRI of the brain
- Young woman presents with neurologic symptoms disseminated in time and space most concerning for multiple sclerosis –> Best diagnostic test is imaging (MRI)
- Key idea: Characteristic imaging findings among patients with multiple sclerosis include white matter lesions in the periventricular region, cortex, cerebellum and spine
- Key idea: MS can also be diagnosed through CSF demonstrating oligoclonal bands, but imaging is less invasive
- Key idea: Classic presentations associated with multiple sclerosis include:
- Internuclear ophthalmoplegia: Lesion to MLF prevent one eye from fully adducting
- Optic neuritis: Painful blurry vision loss with loss of color vision
40) A 37-year-old woman comes to the physician for a follow-up examination 3 weeks after operative repair of a circle of Willis…
Frontal
- Young woman with recent brain surgery presents with behavior changes and lack of motivation, concerning for a frontal lobe injury
- Key idea: Classic Phineas Gage story pertains to patient with damage to the frontal lobe who survived but had persistent personality disorder with trouble with planning/organization and emotional lability
- Occipital lobe injury –> Visual loss/changes
- Parietal lobe injury –> Hemineglect, sensory issues
- Temporal lobe injury –> Hearing problems, olfactory problems, memory problems (hippocampus), Wernicke aphasia
41) A 5-year-old girl has the insidious onset of a clumsy gait over the past 3 months. Examination shows pes cavus of…
Tethered spinal cord
- Young girl presents with clumsy gait and is found to have atrophy and abnormal reflexes of the left lower extremity with a sacral tuft of hair concerning for spina bifida complicated by tethered spinal cord
- Key idea: Tethered spinal cord is a defect in which the distal spinal cord is tethered to fixed structures and patient will develop lower extremity symptoms as they grow given the spinal cord will begin to be stretched
- Ataxia-telangiectasia –> Diffuse telangiectasias + Immunodeficiency + Ataxia
- Friedreich ataxia –> Adolescent with progressive ataxia + scoliosis + cardiac problems
42) A 32-year-old woman with AIDS comes to the physician because of a 2-week history of painful burning sensations in her…
Oral nortriptyline
- Young woman with HIV presents with peripheral neuropathy (burning in hands/feet) which can be treated with TCAs (nortriptyline), Duloxetine (SNRI), gabapentin/pregabalin or topical capsaicin/lidocaine
- Key idea: Common causes of neuropathy include diabetes and HIV
43) A 62-year-old man is brought to the emergency department 2 hours after the sudden onset of headache and left-sided weakness…
Hypertensive intracerebral hematoma
- Middle-aged man with history of hypertension on high-dose aspirin presents with progressive left sided weakness and headache found to have left-sided UMN signs and CT scan showing hyperdense products in the right hemisphere, most concerning for a hypertensive bleed/stroke
- Key idea: Hypertension is the #1 risk factor for intracerebral bleeds and tend to affect midline structures (cerebellum, caudate, putamen, etc.)
- Key idea: When a patient presents with suspected stroke, the first step is non-contrast head CT to rule out a potential hemorrhagic stroke that would preclude treatment with thrombectomy vs TPA (alteplase)
- Ways to differentiate between embolic and hemorrhagic stroke include:
- Embolic
- Risk factors: Atrial fibrillation, recent MI (LV aneurysm), carotid atherosclerosis, endocarditis
- Defects at their maximum intensity within first few minutes
- Hemorrhagic
- Risk factors: Hypertension, cerebral amyloid angiopathy, trauma
- Progressive defects over span of hours
- Embolic
44) A physician makes a house call for an 87-year-old woman who is unable to come to the office because of difficulty with transportation…
Measurement of serum vitamin B12 (cobalamin) concentration
- Elderly man presents with subacute history of frequent falls, decreased lower extremity vibration sensation, and lower extremity weakness with a slapping gait, concerning for possible B12 deficiency
- Key idea: B12 deficiency leads to Subacute Combined Deficiency, which leads to damage to Spinocerebellar tracts (leading to ataxia), lateral Corticospinal tracts (leading to lower extremity weakness) and Dorsal columns (leading to loss of vibration and light touch)
- Top causes of B12 deficiency:
- Pernicious anemia (antibodies against parietal cells): B12 deficiency + GI symptoms (gastritis)
- Veganism
- Nutritional deficiency
- Crohn’s disease (–> ileal disease (B12 absorbed in ileum))
45) A 72-year-old woman is brought to the physician by her husband because of visual hallucinations during the past 2 weeks…
Adverse effect of carbidopa-levodopa
- Elderly patient with Parkinson’s disease with recent uptitration of carbidopa-levodopa presents with recent visual hallucinations most concerning for side effect of carbidopa-levodopa
- Key idea: Parkinson’s disease caused by low dopamine levels whereas schizophrenia caused by high dopamine levels, which is why treatments for Parkinson’s disease (which function by boosting dopamine levels) can lead to hallucinations/delusions and treatments for schizophrenia (which function by decreasing dopamine levels) can lead to extrapyramidal symptoms including parkinsonism
- Key idea: In patients with Parkinson’s disease who develop hallucinations from their medications, the first step is to try to decrease the dose –> If they are unable to decrease the dose of medication given severe Parkinson’s symptoms, next step would be to add an atypical antipsychotic with low risk of extrapyramidal symptoms (classically Quetiapine)
46) A previously healthy 62-year-old man has had progressive difficulty with speech and swallowing over the past year…
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- Middle-aged man presents with progressive dysphagia and dysarthria associated with weakness of intrinsic hand muscles found to have signs of UMN weakness (increased reflexes) and LMN weakness (atrophy/wasting) most concerning for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- Polymyositis –> Weakness + Increased CK + Inflammatory signs (fever, ESR/CRP, etc.)
- Botulism –> Patient who ate canned food and has descending weakness
- Guillain-Barre syndrome –> Patient with recent trigger (GI illness, vaccination) who presents with ascending lower extremity weakness + sensory changes + loss of reflexes
- Multiple sclerosis –> Young patient with neurologic symptoms disseminated in time and space
47) A 37-year-old woman with alcoholism is hospitalized for detoxification. On the second day after admission, she has an impaired…
Oral chlordiazepoxide therapy
- Young woman with alcoholism presents for detoxification and develops hallucinations and sympathetic hyperactivity (hypertension, tachycardia, fever) on day 2, most concerning for delirium tremens that should be treated with phenobarbital versus benzodiazepine taper (chlordiazepoxide)
- Manifestations and timing of alcohol withdrawal
- 0-24 hours –> Mild withdrawal
- 12-48 hours –> Seizures
- 12-48 hours –> Hallucinations (visual, auditory, tactile)
- 48-96 hours –> Delirium tremens (confusion, agitation, sympathetic hyperactivity)
48) A 52-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 2-hour history of a diffuse, bilateral, dull headache. He has…
Hypertensive encephalopathy
- Middle-aged man with history of poorly controlled hypertension presents with headache and confusion and is found to have BP > 180/120 with retinal hemorrhages on fundoscopic exam most concerning for hypertensive encephalopathy
- Hypertensive urgency = Severe hypertension (>180/120) without acute end-organ damage
- Hypertensive encephalopathy = Severe hypertension + cerebral edema and neurologic signs/symptoms
- Malignant hypertension = Severe hypertension + retinal hemorrhages, retinal exudates and/or papilledema
49) A 72-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 2-month history of a progressive tremor of his hands. He and his family…
Carbidopa-levodopa
- Elderly patient presents with chronic progressive resting tremor + rigidity + shuffling gait most concerning for Parkinson’s disease that should be treated with dopamine replacement/agonists (such as carbidopa-levodopa)
- Signs/symptoms of Parkinson’s disease can be remembered by mnemonic TRAPS:
- Tremor (resting, can be asymmetric)
- Rigidity
- Akinesia (slow movements)
- Postural instability (can’t catch themselves if they fall)
- Shuffling gait
- Primidone or Atenolol –> Essential tremor (bilateral positional tremor in patient with family history
- Donepezil –> Alzheimer disease
50) A 47-year-old woman comes to the physician because of increasingly frequent headaches during the past 3 months…
Discontinuation of conjugated estrogen therapy
- Perimenopausal woman on conjugated estrogen therapy presents with significant increase in frequency of migraines (throbbing unilateral headaches associated with photophobia, nausea, etc.) and therefore should stop using estrogen
- Key idea: Conjugated estrogen therapy (like pregnancy and hormonal fluctuations with menses) can lead to worsening of migraines
- Key idea: Indications for estrogen replacement therapy among perimenopausal symptoms are intolerable menopausal symptoms (hot flashes, sleep problems, etc.)
We are not affiliated with the NBME, USMLE or AAMC.
The answer explanations may not be reproduced or distributed, in whole or in part, without written permission of Step Prep.
